Cheese Production and Plastic Packaging
Cheese Production and Process
Cheese production has been carried out for years. The techniques used in cheese making can vary depending on the type of cheese, the source of milk used, the geographical region, and even the country. The main components of cheese making include milk, rennet, starter cultures, and cheese cultures. The process of cheese making involves pasteurizing the milk, fermenting it, forming cheese curds, and finally, aging the cheese.
Cheese is prepared by processing the curds formed by coagulating (the process of liquid turning into curds) milk, cream, skimmed or partially skimmed milk, buttermilk, or a combination of these products with suitable enzymes and/or lactic acid, and then by appropriately processing the drained whey.
There ara more than 2500 cheese types and varieties in the world. Cheeses are classified into very hard, hard, semi-hard, semi-soft, and soft categories based on their moisture content. They are also grouped into full-fat, fatty, semi-fat, and fat-free categories based on their fat content.
The cheese production scheme is as follows.
Raw milk -> Cheese milk -> Coagulated cheese-> Curd -> Feta Cheese
· After the raw milk is selected, it is pre-processed, where the cleaning process is applied and it goes to the heat treatment stage. In heat treatment, milk undergoes pasteurization.
· A curd is obtained from the resulting cheese milk with additives.
· This curd is first cut, stirred, and heated. Then, acidity development is ensured. The whey is separated, and this process is called syneresis.
· At the curd formation stage, acidity development is emphasized and special processes such as boiling are applied. Salt can also be added according to the desired flavor. The cheese is transferred to a mold and pressed to shape it during the molding stage.
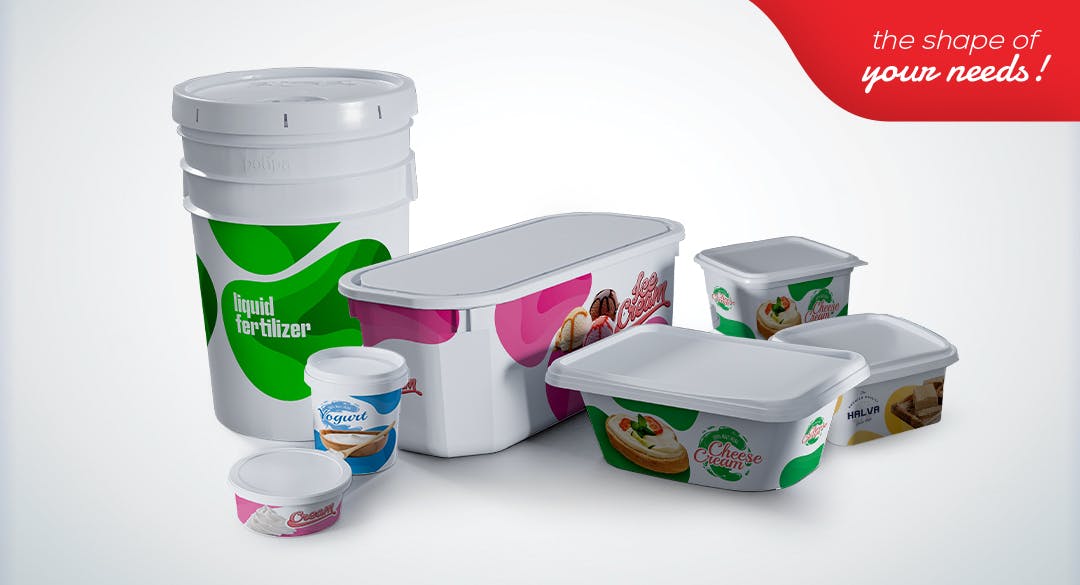
· The resulting fresh cheese is packaged if desired. However, most varieties are salted, secondary culture is added and cheese aging and maturation is waited. Afterwards, the packaged cheese is ready to meet the consumer.
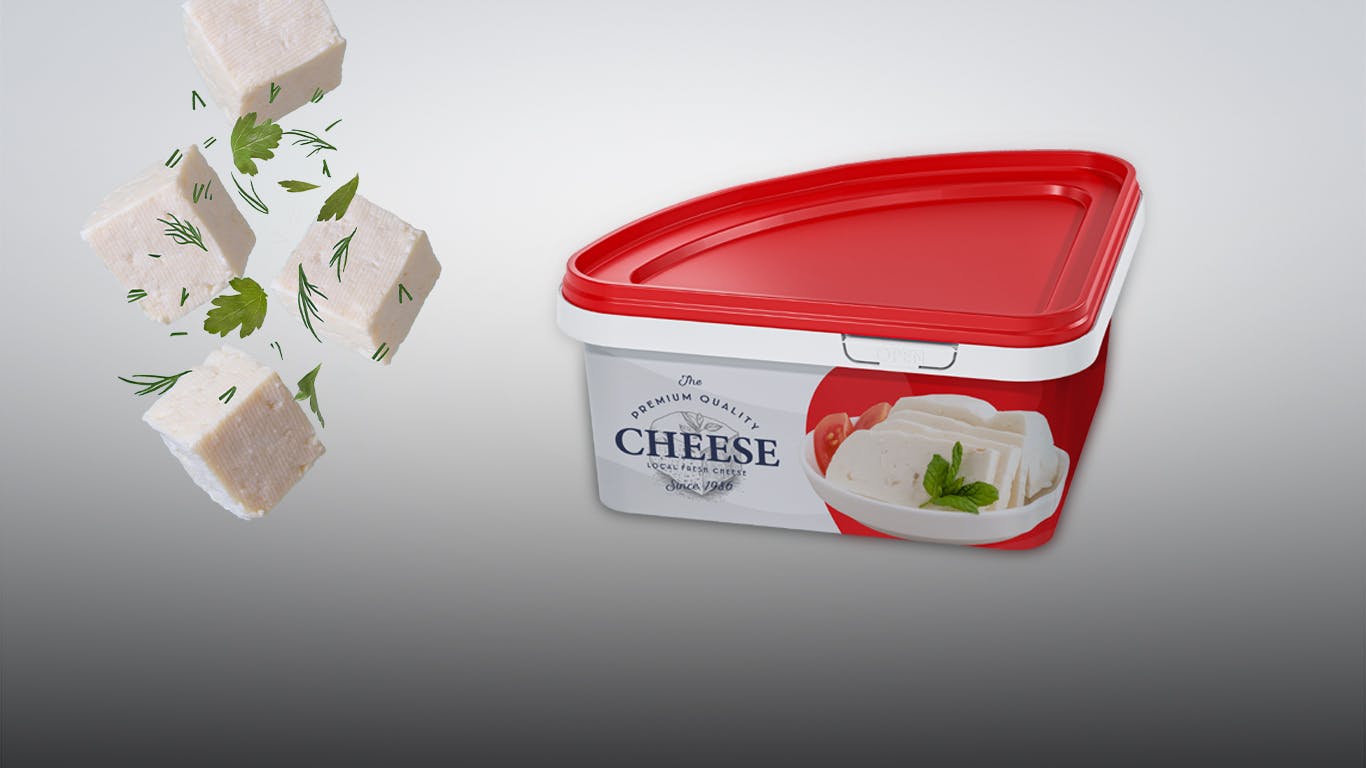
Packaging Need for Cheese / Importance of Cheese Packaging
The importance and benefits of the plastic packaging used in cheese can be evaluated from various aspects.
Packaging for extended shelf-life / Protection: Plastic packaging ensures the protection of cheese against external factors. Elements such as air, moisture, light, and microorganisms can have a negative impact on the quality of cheese. Plastic packaging helps to protect the cheese from such factors, allowing it to be stored fresh and safely for a longer period of time.
Hygiene: Plastic packaging ensures that the cheese is preserved in hygienic conditions. The packaging prevents the contamination of cheese by microorganisms that may come into contact with it after the production process, ensuring the microbiological safety of the cheese.
Portability: Plastic packaging enables the cheese to be transported easily and conveniently. The packaging allows the cheese to be transported without breaking, crushing, or deforming, thereby preserving its shape, texture, and flavor.
Information: Plastic packaging provides information about the cheese to the consumer through labels on them. The packaging may contain details such as the type of cheese, producer information, storage conditions, and usage recommendations. This information helps consumers make informed choices and properly store the cheese.
Eco Friendly Packaging Solutions: Plastic packaging can be made from eco-friendly materials. By using recyclable plastics, it is possible to reduce packaging waste and protect natural resources.
The technology used to prevent the label from coming off or fading on the packaging selected for cheese is called IML (In-Mold Labeling). Due to the high water or fat content in cheeses, IML is used to ensure that the label remains attached to the packaging and that the text does not fade in any way. This technology allows the label on the packaging to stay intact for a long time.